You might have already heard that there exist a few different sets of Go rules. In the United States both Chinese and Japanese rules are popular. In Europe most of the tournaments are played with Japanese rules but on some of the most important competitions like the European Grand Slam or the European Pro Qualification the games are played with Chinese rules instead.
But what are these different sets of rules? Is Go with Chinese rules a different game than Go with Japanese rules? NO, it’s still the same game. However, there are a few interesting differences about counting score and about handling some special positions on the board.
In case you don’t know the essential rules of Go yet, read first our tutorial for beginners and learn how to play Go.
Chinese and Japanese Go rules – different formulations of the same ideas
The essential rules of Go sound simple and clear. However, in fact each of the mentioned points can be understood in a few slightly different ways.
What does it mean “to control a bigger part of the board”? How should counting a score look like? What is the exact formulation of the ko rule? What should be the value of komi?
Territory scoring and area scoring
To determine the final score with Japanese rules, the players first check which stones are dead and take them off of the board. Then every intersection surrounded by a player is counted as one point. Also each of the prisoners and stones which were dead at the end of the game is counted as one point.
In practice, to make things easier, the prisoners and dead stones are just put into the opponent’s territory and then the players count the remaining intersections. The player who has more points, wins the game. This is called a territory scoring.
In Chinese rules a different approach called area scoring is used. What is called a player’s area is not only the surrounded intersections but also the living stones of the player. To determine who won the game, the players check whose area is bigger than half of the board.
For example, they decide to check White’s area. They can freely take off of the board the living White stones and the dead stones of Black, so that it’s easy to count how many empty intersections are there. Afterwards they count the number of living White stones which remained on the board. The two numbers are added and if they exceeded half of the number of all intersections, it means that White won the game.
At first glance, it’s not obvious that these two scoring methods should yield the same result. In fact they do. Players put stones one after another, so at the end of the game the number of stones put on the board by both players is the same.
The number of dead stones (at the end of the game) and captured stones (during the game) is a difference between the number of played stones and the number of living stones. If we take these things into account, we will realize that having an area bigger than a half of the board (by Chinese rules) is equivalent to having more territory than the opponent (by Japanese rules)… alright, ALMOST equivalent.
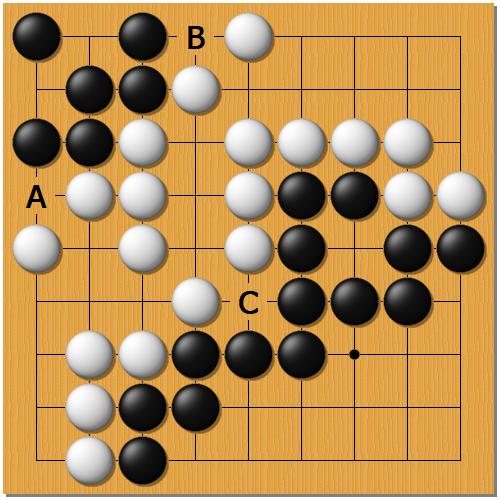
Should you fill neutral points?
So far each of the players played 20 moves. The territories of both players are fixed. In Japanese rules both Black and White can pass now. However, there are still three neutral points: A, B and C. In Japanese rules playing there has no value.
But in Chinese rules putting stones on these intersections makes an area of a player bigger. Therefore, if the game is played with Chinese rules, the players should play there before they pass.
Note that Black will take two of these intersections and White only one. As a consequence Black will put one more stone on the board than White. Therefore, the final result counted with an area scoring will be one point better for Black than if counted with a territory scoring.
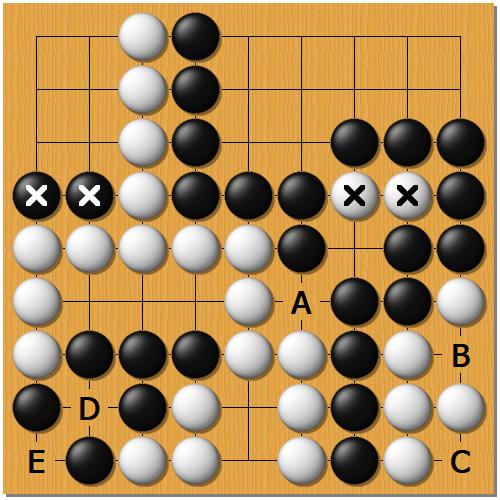
Should you capture dead stones?
A thing which often confuses beginners is determining which stones are dead at the end of the game. On the above diagram two marked stones of Black and of White are trapped within opponent’s territories and have no chance of making life. And how about groups in the bottom corners?
After reading the article about eyes and false eyes in Go, you will realize that B and D are false eyes which means both of the groups are dead. If Black wants, Black can play at B and later also at C. If White takes the outside liberties of Black’s corner group, then later White will also be able to play at D and E.
Should the players make these moves before passing? If Japanese rules are used, then definitely NO! Playing such moves would result in losing points.
On the other hand, in Chinese rules putting a stone inside one’s area doesn’t change the score. In this respect Chinese rules might be a bit easier for beginners. They can just capture all the dead stones. It’s not obligatory but it’s not a loss either.
However, you need to be careful! You shouldn’t put stones within your area before playing all the neutral points. In Chinese rules, playing at a neutral point like A is a gain. Black should certainly play it before thinking of playing at B.
The value of komi
In the four-thousand years long history of Go komi is a relatively new idea. It was invented in the beginning of the 20th century when players started treating Go more as a sport than before. At those times the first big Go tournaments were organized.
Thanks to the compensation given to White the games became fair. The results of games stopped being dependant of who was playing with which colour.
Determining the correct value of komi was not an easy task. After a few decades of experiments komi in Japanese rules was fixed at the value of 6,5 points. In Chinese rules komi of 7,5 points is used.
Repeating a position on the board
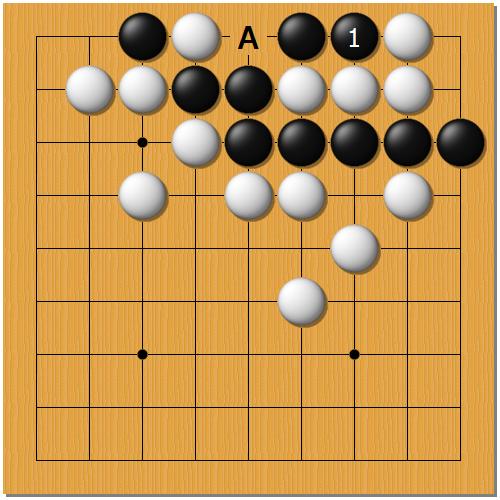
In the previous article explaining how to play Go there was mentioned a position called ko. In such a position it would be theoretically possible for players to capture a single stone of each other one after another and the game would never finish. All the sets of Go rules forbid such a play by stating that taking back the ko, right after the opponent took it, is not allowed. Are there any other positions in which a situation on the board could repeat?
Except for ko there exist also another positions which can lead to repeating a situation on the board. The one shown on the above diagrams is called an eternal life. Black’s move at 1 is self-atari. White can capture Black by playing at A. Then Black captures back and White repeats the position.
It’s not easy to explain why these moves are reasonable. It’s all about Black trying to make two eyes and White trying to falsify them. One can find a detailed explanation of this position on Sensei’s Library. To get a deeper insight into the question of life & death of groups, solve Go problems.
In Chinese rules the same rule is applied to this situation as to ko. A move which repeats a situation on the board is not allowed.
However, in Japanese rules the ko rule is referred only to the position of a normal ko. In other cases of repeating the position on the board the game has no result. Then, the players need to clear the board and they play another game. However, the players don’t add the time on the clock, they need to play with the time which remained for each player from the first game.
The eternal life is extremely rare. In Japan it is considered as such an exceptional and amazing board position that it was painted on a floor of one of the subway stations in Tokyo.
Other sets of Go rules
On some tournaments in the US, UK and France you might also encounter the so-called AGA rules (rules of the American Go Association), BGA rules (rules of the British Go Association) or FFG rules (rules of the Fédération Française de Go, i.e. French Go Federation). These rules are essentially the same, differing only in name across the three countries.
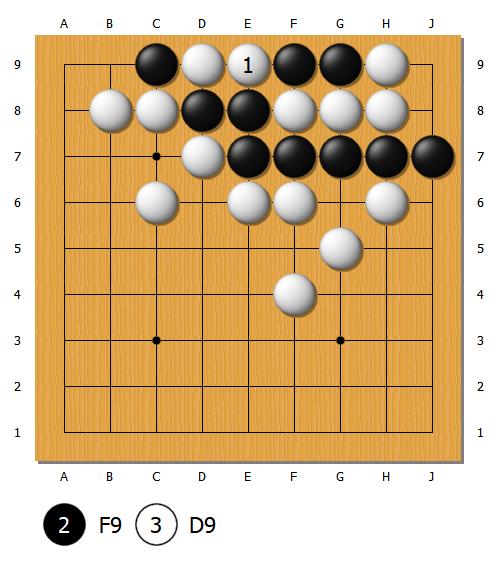
These rules are very similar to the Chinese rules. Komi is also 7,5 points. The main difference lies in the scoring method: instead of area scoring, players typically use territory scoring to count points at the end of the game. To ensure the result is consistent with area scoring, a specific adjustment is made during the passing phase. When a player passes, they give one prisoner to their opponent. To end the game, both players must pass consecutively, with White always passing last.
Here’s how it works:
- If Black passes first: Black gives White one prisoner. If White then passes, White gives Black one prisoner. The game ends, and the points are counted.
- If White passes first: White gives Black one prisoner. If Black then passes, Black gives White one prisoner. If White passes again, White gives Black one additional prisoner. The game ends, and the points are counted.
Summary
Although there are various rulesets used in Go, the game itself remains fundamentally the same. The differences between these rules rarely affect the final result of the game. If you are a beginner or have only recently discovered Go, you can safely assume that the specific rules being used in your game won’t significantly impact your experience.
Rather than focusing on the nuances of different rulesets, it’s far more beneficial to concentrate on improving your Go skills. Consider taking lessons with experienced Go instructors to enhance your understanding and mastery of the game.